Mapping/SLAM (JMI) and Localization (WAI) are key ingredients for autonomous vehicles to perform any task in real-world operations. Creating a map (SLAM) of the environment requires a skillset to get a global position similar to what a GPS provides. The technology works without any structural support or changing the operating area. Mapping large areas can be achieved in a few steps, and the localization outputs stable high accuracy results even in challenging situations. As localization depends on a well-calibrated sensor setup and meets client expectations of accuracy and speed, we have set a minimum configuration for specific tasks. The modular software supports a wide range of standard sensors and combinations.
Tasks: Indoor/Outdoor Localization in 2D (x, y, theta) or 3D (x, y, z, yaw, pitch, roll)
Sensors: LIDAR (Ouster, Velodyne, SICK, …), Depth Camera (Intel Realsense, Azure Kinect, …), Inertial Measurement Units
JMI – Mapping
Mapping is typicaly done with a SLAM approach by recording the operating area once and generating a map.
- Suitable for large and complex areas
- Very fast processing (faster then real time)
- No post-processing required
- Simple operation and no skills required
- Output are point cloud representations (x, y, z)
- Web Application Interface
WAI – Localization
The localization unit requires a predefined mapped area and outputs the position of the localization unit or in a desired vehicle coordinate frame.
- Standard accuracy with one LIDAR < 2 cm in position and < 1° in orientation
- High precision accuracy with multiple sensors (on demand)
- Performs in highly dynamic environments (changes above > 80%)
- Easy fusion of several sensors and types of sensors
- Interface via ROS, TCP, Modbus, CAN, REST, VDA5050
Technology
SLAM UNDER THE HOOD
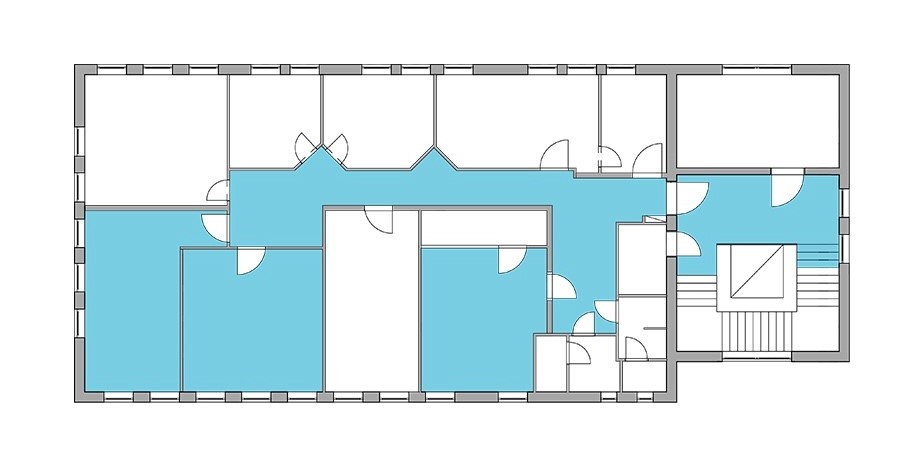
SLAM stands for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. It is a method of creating a map which finds its applications in robotics, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality and many other related fields.
At its core, SLAM is designed with the overarching goal of generating a comprehensive map of an unfamiliar environment, while concurrently tracking the precise location of a robot within that same environment. This dual functionality is essential in enabling autonomous systems to navigate unfamiliar surroundings with a high degree of accuracy.
Successfull implementation of SLAM, involves careful consideration of multiple factors such as:
- Calibration of sensors
- Fusion of data from different sensors
- Managment and efficiency of real time computational demands
- Accurate localization
- Consideration of dynamic changes
Achieving accuracy and reliability in SLAM requires an approach that addresses all challenges, ensuring effective mapping and localization in real-world applications.
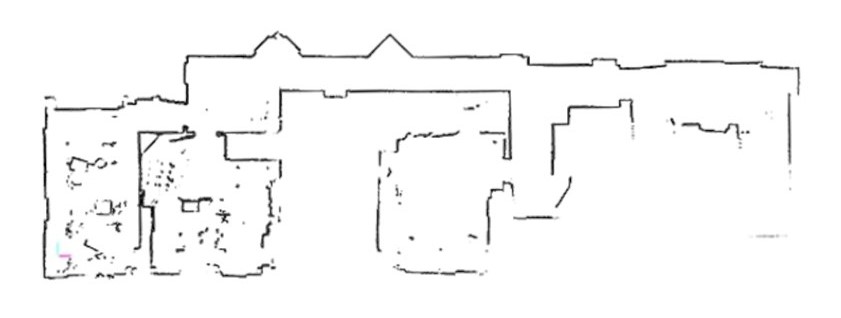
Clear contours and features
The accuracy of maps generated by SLAM is crucial for autonomous navigation. A map with clear contours results in better localization, making it easier for robots or other automated systems to move around. A map with fuzzy contours can lead to erroneous navigation, increasing the risk of problems and failures.
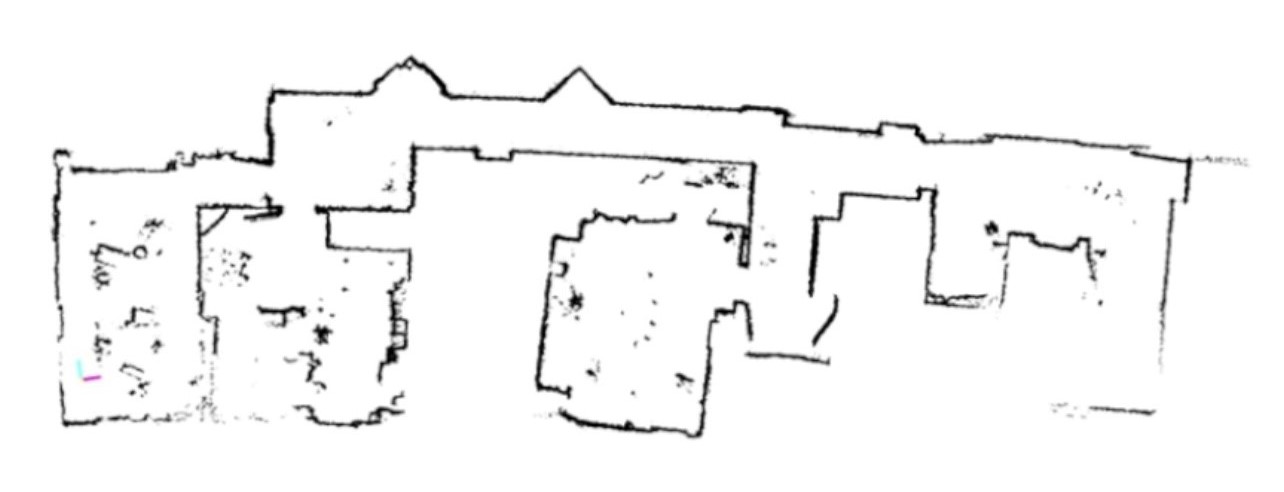
Error case – Bending
Bending can cause the system to misinterpret the environment, possibly leading to incorrect decisions or actions. Precise relative measurements ensure that the mapping algorithm correctly detects similar data points, enhancing the clarity and accuracy of the generated map.
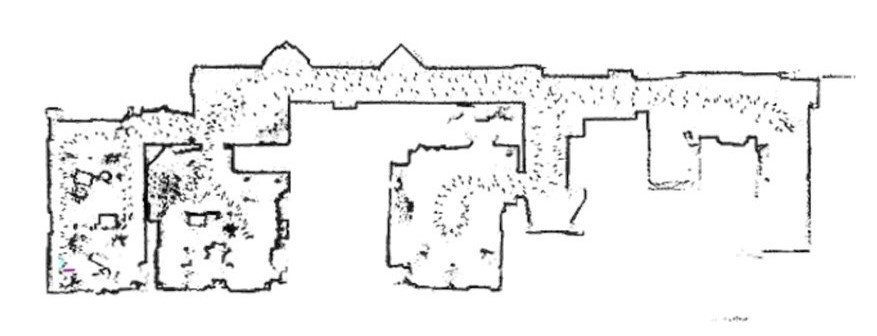
Error case – Filtering
Data filtering is an essential part of SLAM. Setting up a valid filter chain helps remove noise from the sensor data, making the mapping and localization process more reliable. Using inappropriate or insufficient filters can compromise the quality and accuracy of the SLAM output.
Frequently Asked Questions
FIND QUICK ANSWERS
What types of licenses do you offer?
We provide solutions for individual systems and entire product lines. Click here to learn more about our licensing system and find the best solution for your needs.
How long does the integration take?
The time required for integration depends on the specific application. It usually takes a day or two.
Can I do the integration myself?
Yes, due to the plug&play readiness, you can integrate our localization component on your own.
Can the end customer use the localization without assistance?
Yes, absolutely! After the first integration, the robots can easily deployed directly to the end customer and can then be used without further assistance.
Is the localization compatible with my setup?
We process data and in-depth information from different sensors and communicate with various platforms and setups. For additional compatibility questions, feel free to contact us.
Videos
EXPERIENCE THE TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION
GET A QUOTE


